The Endocannabinoid System (ECS) is a complex and crucial biological system, the existence of which is vital for the proper functioning of the body. It plays a fundamental role in a wide variety of physiological processes, with a highlight on regulating body systems to maintain homeostasis or a state of balance. This balance is necessary to respond appropriately to internal and external changes, ensuring that the body functions optimally.
The ECS is a regulatory system linked to major organs, the immune and nervous systems, and certain areas of the brain. The endocannabinoid system influences nearly all major physiological functions, including the regulation of the nervous system, the immune system, the cardiovascular system, and the digestive system, among others.
How and When Was the Endocannabinoid System Discovered?
The discovery of cannabinoids was the key tool for uncovering the ECS. Although CBN is believed to be the first cannabinoid isolated in the late 19th century, it wasn't until the late 1980s that the existence of "cannabinoid" binding sites began to be considered.
By then, CBD and THC had been isolated (mid-20th century), and due to its psychoactive effect, research had focused on THC. Interestingly, these studies and a broad set of hypotheses surrounding the action of this cannabinoid in the body led to the assumption that its molecules directly bound to specific sites in the body.
In 1988, researchers from the Pharmacology Department of the School of Medicine at the University of San Luis, conducting experiments on rat brains using radiolabeled molecules, identified the first binding site of a THC analog. Just two years later, other research identified the CB1 receptor, and very soon after, another team managed to identify the CB2 receptor.
How Is the ECS Structured?
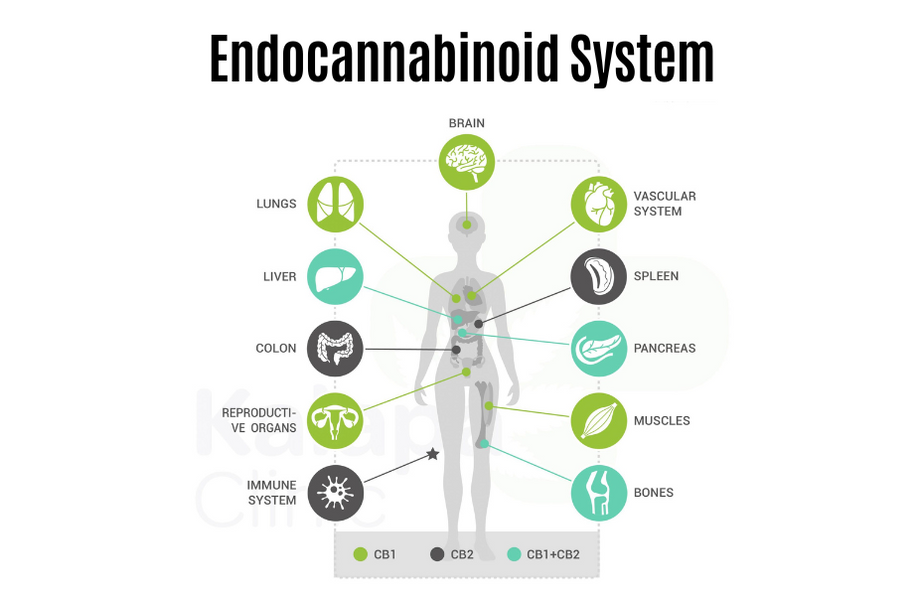
Since then, research has continued to advance, and today it is known that the ECS is composed of cannabinoid receptors, endocannabinoids, and enzymes involved in various physiological processes. These components are located in different parts of the body, including the immune system, the nervous system, the skin, and the bones.
- Cannabinoid Receptors: The ECS includes two main types of receptors: CB1 receptors, primarily found in the central nervous system, and CB2 receptors, mainly located in the immune system and peripheral tissues. These receptors respond to both endocannabinoids and external cannabinoids, such as those found in the cannabis plant.
- Endocannabinoids: Endocannabinoids are chemicals naturally produced by the body. The two main endocannabinoids are anandamide and 2-arachidonoylglycerol (2-AG). These compounds act as chemical messengers that bind to cannabinoid receptors to regulate various biological functions, such as pain response, appetite, mood, and sleep.
- Enzymes: Specific enzymes, such as FAAH (fatty acid amide hydrolase), break down endocannabinoids after they have fulfilled their function. This breakdown is essential to prevent elevated levels of endocannabinoids in the body.
How Does the ECS Function?
The endocannabinoid system functions in a straightforward manner. While controlling the body's internal systems, it facilitates the release of endocannabinoids when it detects an imbalance. These endocannabinoids bind to receptors scattered throughout the body, triggering a variety of biological functions.
Upon contact with cannabinoids, these receptors are activated, stimulating various physiological responses in the body, such as in anxiety, pain, stress, and many other health disorders.
The endocannabinoid system employs a principle similar to that of a lock and key. This means that different receptors located in the body are activated only in the presence of a cannabinoid with a specific profile or shape. In other words, the receptor is activated only by a cannabinoid that perfectly fits into the lock of the receptor.
While definitive conclusions are not yet available because the study of the Endocannabinoid System is constantly evolving, it is currently known to be related to some of the most important functions of the body, including memory, appetite, energy balance, metabolism, immune function, and sleep, among others.
 US Dollars
US Dollars